A Deep Dive into Toyota's Batteries
Toyota is betting on a specific battery technology for electric vehicles. Will it manage to deliver?
Welcome to Lithium Horizons! This newsletter explores the latest developments, companies, and ideas at the frontiers of energy materials. Subscribe below to get the next article delivered straight to your inbox.
‘‘It is in Toyota's DNA that mistakes made once will not be repeated.’’
― Akio Toyoda, Chairman of Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota has been sending mixed signals regarding batteries for some time. On one hand, they periodically announce breakthroughs in battery technology, while on the other, they dismiss batteries in favor of hydrogen. This contradiction persists, raising questions on how a company as renowned as Toyota can contradict itself so frequently.
The explanation lies in the significant risk Toyota took with hybrid vehicles in the late 1990s. This gamble paid off handsomely, establishing Toyota as the global leader in hybrid electric vehicles. However, they soon missed out on the trend towards fully battery powered electric vehicles (BEVs) using lithium-ion technology. While competitors were rapidly advancing BEV development, Toyota sought to maintain its edge in hybrid technology, seemingly reluctant to acknowledge that fully electric vehicles might be the superior technology.
Toyota is not contradicting itself; rather, it is engaging in corporate double-speak, leveraging its strengths while simultaneously developing new technologies in hopes of gaining a fresh competitive edge. The question is which one?
What is Toyota currently working on? What do they aim to achieve? What is the future vision for Toyota? These questions inspired this article, where we delve into Toyota's involvement with batteries. We'll start with the history of Toyota's battery engagement, then move on to explore their new technology roadmap, their solid-state battery initiatives, and their patents.
Let's dive in! 🔋
NOTE: if you are reading this in your email client, the text may be clipped due to its length. Click on "View entire message" at the bottom of your email to read the whole article, or open it in your browser or Substack app.
The History of Toyota’s Involvement with Batteries
Toyota's involvement with batteries didn't start with electric vehicles but with the foundational need for reliable starting batteries in their combustion engine vehicles. Over the years, Toyota has refined its battery technology, ensuring vehicles start reliably in various conditions.
The real turning point came with the introduction of the Prius in 1997, which utilized a nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) battery.1 This was a significant step as it marked Toyota's commitment to hybrid technology. Just a year earlier, in 1996, Toyota established Prime Earth EV Energy as a joint venture with Panasonic to develop these batteries.2 The NiMH battery was chosen for its balance of energy density, longevity, and safety over the then-developing lithium-ion technology, which was less mature and much more expensive.
By the late 2000s, as lithium-ion technology became more reliable and cost-effective, Toyota began exploring the use of lithium-ion batteries. It established the Battery Research Division in 2008 and gradually introduced lithium-ion batteries in various models, including the latest iterations of the Prius and other hybrid models.
Toyota's entry into the fully electric vehicle market came much later. In 2021, it established Prime Planet Energy & Solutions as a new joint venture with Panasonic to accelerate the development of batteries for use in different products. Soon after, in 2022, Toyota introduced the bZ4X battery powered electric vehicle.
Toyota’s New Battery Technology Roadmap
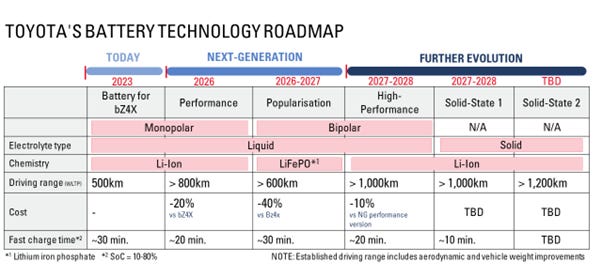
In 2023, Toyota announced its new battery technology roadmap, setting out plans for battery development up to 2030. It promises several new batteries:
Performance battery: Utilizing a liquid electrolyte and lithium-ion chemistry, this battery promises a 20% cost reduction for new electric vehicles compared to the bZ4X model. It aims to charge from 10% to 80% in 20 minutes or less, offering a driving range of 800km.
Popularisation battery: Also using a liquid electrolyte with lithium-ion chemistry, this version incorporates an lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cathode and a bipolar structure. It should reduce costs by 40% compared to the bZ4X, achieve a 10% to 80% charge in 30 minutes, and provide a range exceeding 600km.
High-performance battery: This type features a high nickel NMC cathode and a bipolar structure with liquid electrolyte, aiming for a driving range beyond 1000km. It offers an additional 10% cost reduction over the Performance battery and supports ultra-fast charging in under 20 minutes.
Solid-state batteries: Scheduled for mass production post-2027, these batteries are designed to offer over 1000km of range with a fast charging capability of just 10 minutes.
This roadmap essentially outlines a new platform for BEVs, akin to what Ford is developing. The focus here isn't solely on the battery itself but also on how the battery integrates into the vehicle's design. For instance, you may have observed that electric vehicles often have a higher base due to the battery pack running underneath them. Toyota is making efforts to decrease the height of these batteries to lower the vehicle's frontal area, which in turn reduces the drag coefficient. Aerodynamics are crucial in defining the driving range of vehicles, so in the pursuit of maximizing BEV range, optimizing the drag coefficient is key. Toyota's target is to slim down the battery pack's height from 15 cm to 10-12 cm.
Therefore, Toyota is pursuing a holistic approach, a complete vertical integration. They are considering everything from the materials used in the batteries, to their manufacturing processes, and their integration into vehicles. Toyota aims for a complete solution: to redefine what an electric vehicle company is… starting from 2026!


